Bronchiolitis Interstitial Lung Disease
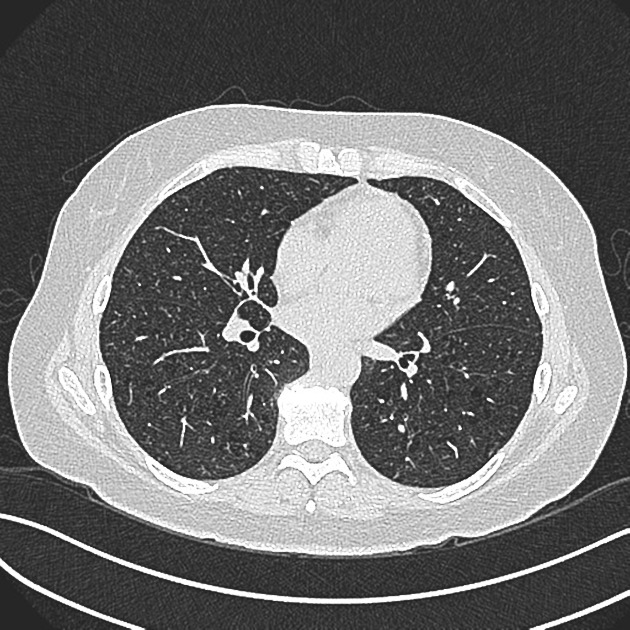
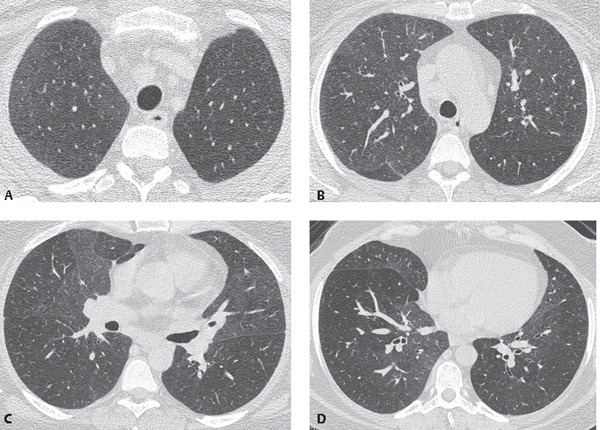
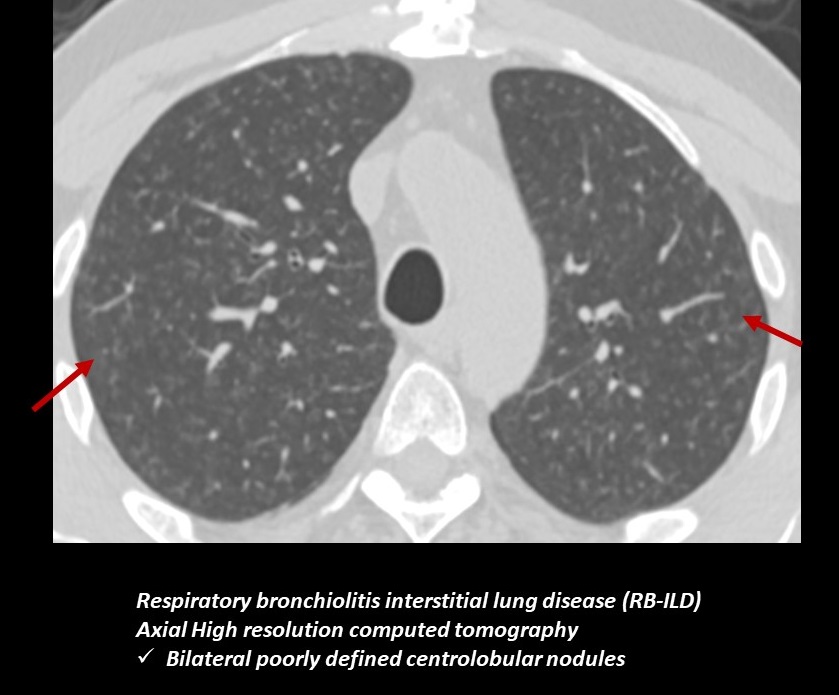
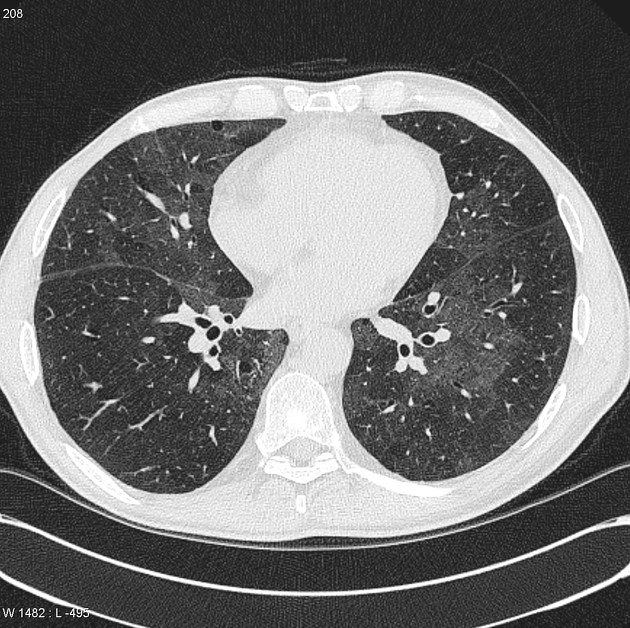
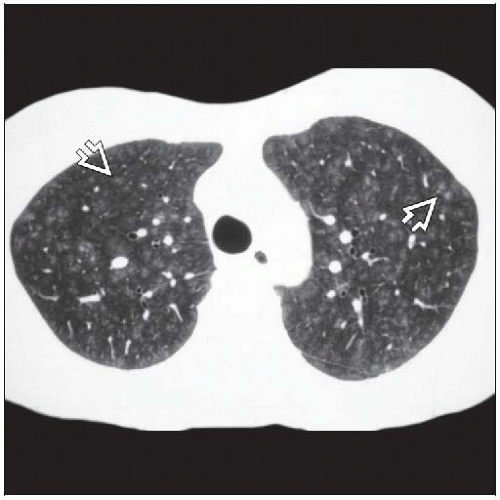
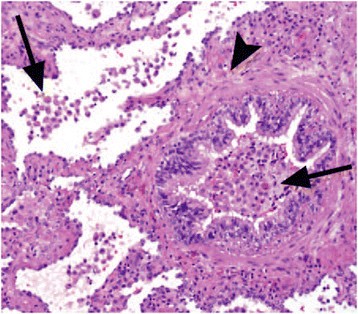
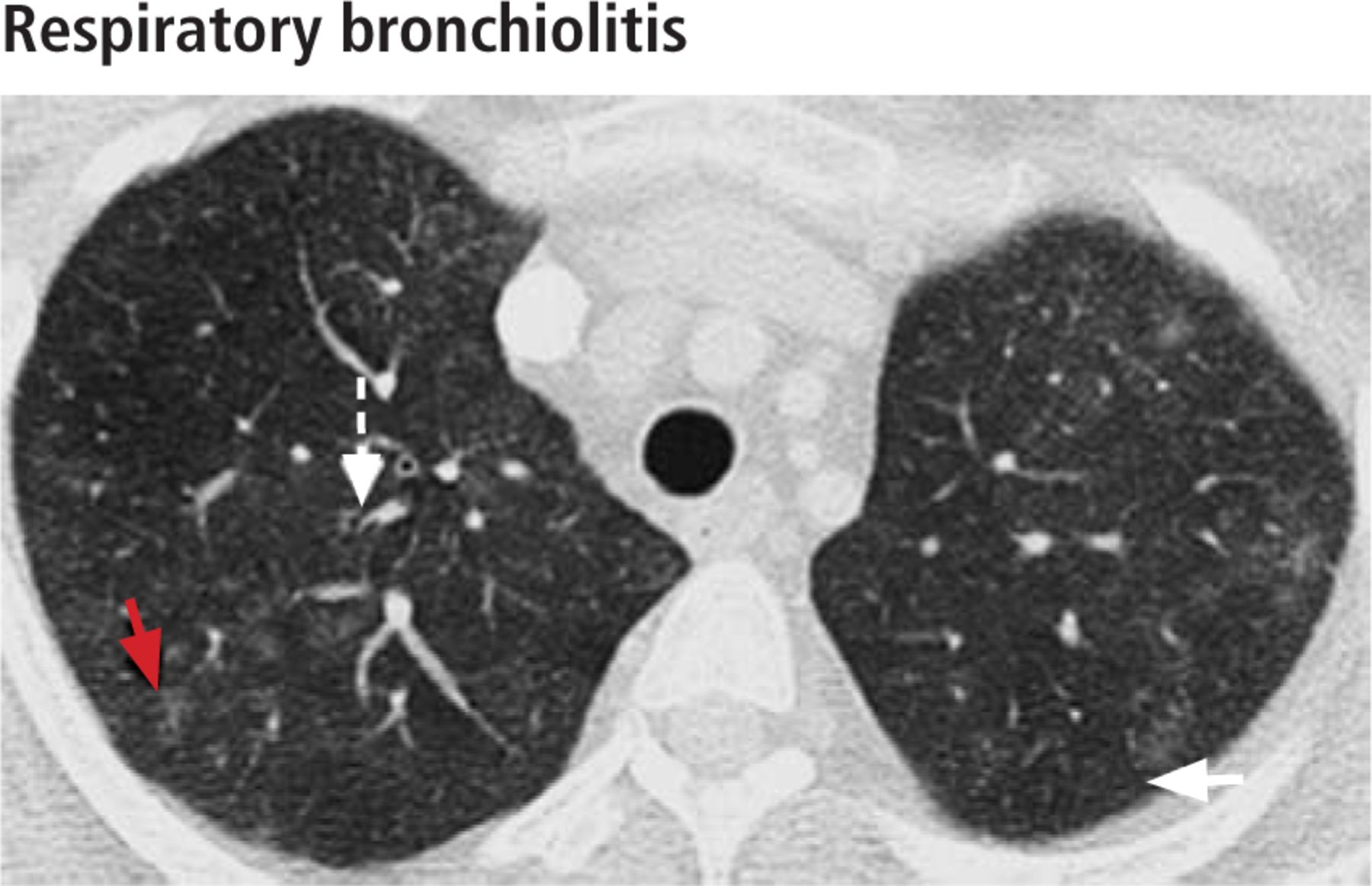
Bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease. Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is categorized as a smoking-related interstitial pneumonia and is one of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias IIP 1. Crackles or wheeze are typical findings on listening to the chest with a stethoscope. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is characterized by greater accumulation of macrophages in the bronchioles and accentuated peribronchiolar interstitial inflammatory process 3.
Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease includes more than 200 different conditions that cause inflammation and scarring around the balloon-like air sacs in your lungs called the alveoli. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is an inflammatory lung disorder associated with cigarette smoking.
The onset is usually insidi. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is a rare mild inflammatory pulmonary disorder that occurs almost exclusively in current or former heavy smokers usually between the third and sixth decades most likely with no gender predilection. RB-ILD respiratory bronchiolitis-associated intersti-tial lung disease Desquamative interstitial pneumonia DIP and respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD are associated with cigarette smoking and represent two of seven entities that are.
Respiratory bronchiolitisassociated interstitial lung disease RBILD is a syndrome of small airway inflammation and interstitial lung disease occurring in smokers. Some smokers with clinical physiologic and radiographic evidence of an interstitial lung disease ILD were also noted to have similar histopathologic features on surgical lung biopsy. The other major IIPs include idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF nonspecific interstitial pneumonia NSIP desquamative interstitial pneumonia DIP another.
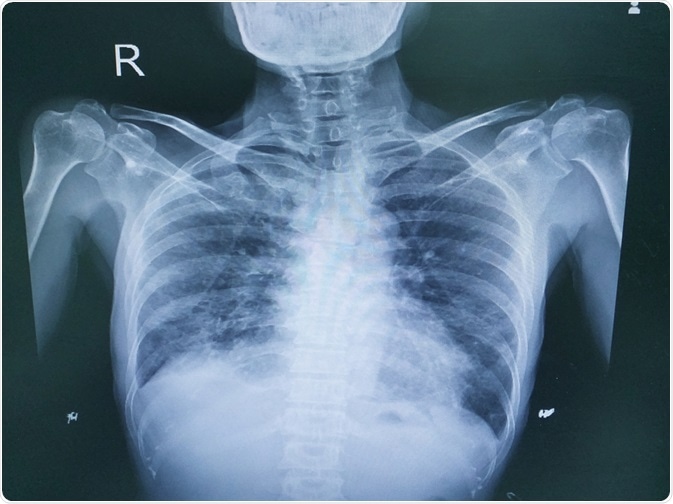
Small airway disease is rarely reported in IgG4-related lung disease IgG4-RLD. Chest x-ray high-resolution CT and sometimes lung biopsy are needed for diagnosis. The onset is usually insidious with exertional dyspnea and progressive persistent cough which may be nonproductive.
This condition has only recently been described and distinguished from desquamative interstitial pneumonitis which it closely resembles. Although insidious respiratory symptoms are more common. Treatment is smoking cessation.
The concept of respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease RBILD was introduced to explain the presence of interstitial lung disease in individuals whose only finding on surgical lung biopsy was smokers respiratory bronchiolitis RB. Respiratory bronchiolitisassociated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is a rare pulmonary disorder that occurs almost exclusively in current or former heavy adult smokers usually between ages 30 and 70 years.
It concerns alveolar epithelium pulmonary capillary endothelium basement membrane and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues.
Some smokers with clinical physiologic and radiographic evidence of an interstitial lung disease ILD were also noted to have similar histopathologic features on surgical lung biopsy. The concept of respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease RBILD was introduced to explain the presence of interstitial lung disease in individuals whose only finding on surgical lung biopsy was smokers respiratory bronchiolitis RB. This clinicopathologic syndrome was termed respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease. Respiratory BronchiolitisAssociated Interstitial Lung Disease Respiratory bronchiolitis RB is a histopathologic lesion of the small airways that is common in cigarette smokers97 In some smokers an exuberant form of RB occurs as a clinical and radiologic manifestation of diffuse ILD. Although insidious respiratory symptoms are more common. Treatment is smoking cessation. This clinicopathologic syndrome called respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD occurs almost exclusively in heavy cigarette smokers. Crackles or wheeze are typical findings on listening to the chest with a stethoscope. Some smokers with clinical physiologic and radiographic evidence of an interstitial lung disease ILD were also noted to have similar histopathologic features on surgical lung biopsy.
Interstitial lung disease ILD or diffuse parenchymal lung disease DPLD is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium the tissue and space around the alveoli air sacs of the lungs. This condition has only recently been described and distinguished from desquamative interstitial pneumonitis which it closely resembles. Some smokers with clinical physiologic and radiographic evidence of an interstitial lung disease ILD were also noted to have similar histopathologic features on surgical lung biopsy. The onset is usually insidi. Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is categorized as a smoking-related interstitial pneumonia and is one of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias IIP 1. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is an inflammatory lung disorder associated with cigarette smoking. The pulmonary manifestation of this disease is highly variable and may mimic lung cancer pneumonia interstitial lung disease ILD sarcoidosis and so forth.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Bronchiolitis Interstitial Lung Disease"