how to increase blood flow to placenta
 How To Naturally Improve Circulation During Pregnancy | Walnut Hill OBGYN
How To Naturally Improve Circulation During Pregnancy | Walnut Hill OBGYNCoronavirus (COVID-19): Silence Silence Silence of Fetal Growth What is the restriction of fetal growth (FGR)? The restriction of fetal growth (FGR) is a condition in which an unborn baby (fetus) is less than expected for the number of weeks of pregnancy (age of pregnancy). That's it. It is often described as an estimated weight less than the 10th percentile. This means that the baby weighs less than 9 of every 10 babies of the same gestational age. newborn Babies with FGR can be called "small for gestational age. " FGR can start at any time during pregnancy. With FGR, the baby doesn't grow well. FGR can affect the overall size of the baby and the growth of organs, tissues and cells. This can cause many problems. But many newborns that are small can be small. They may not have problems. What FGR cause? Many things increase the risk of FGR. These include problems with placenta or umbilical cord. The placenta can't fix well. Or the flow of blood through the umbilical The cord can be limited. Factors in both the mother and the baby can cause FGR. Factors in the mother that can cause FGR include: High blood pressure or other heart disease and blood vessel Diabetes Very few red blood cells (anemia) Long-term lung or kidney conditions Autoimmunity conditions such as lupus Very low weight A lot of weight excess (obese) urine nutrition or weight gainAlcohol or drug useCigarette smokingThe factors that can cause a throttle A pregnant woman has no symptoms of FGR. But a baby with FGR can have a certain signs after birth, such as: Low Weight at Birth Low Blood Sugar Levels Lower Body Temperature High Level of Red Globe Problems Fighting Infections How is FGR Diagnosed? One of the main reasons for regular prenatal exams is to make sure your baby is growing Okay. During pregnancy, your baby's size is calculated in different ways, including: Financial height. To check the funding height, your health care provider measures from the top of your pubic bone to the top of your uterus (fundus). Height of the background, measured in centimeters (cm), is equal to the number of weeks of pregnancy after week 20. For example, at 24 weeks of gestation, its background height should be about 24 cm. If the bottom height is less than expected, it can mean FGR. If your health care provider thinks you have FGR, you will have other tests. These are include: Fetal ultrasound. Estimating fetal weight with ultrasound is the best way to find FGR. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the baby in the uterus. The sound waves won't hurt you or the baby. Your healthcare provider or a technician will use the images to measure the baby. A diagnosis of FGR is based on the difference between real and expected measures at a certain gestational age. Ultrasound Doppler. You may also have this special ultrasound type to diagnose FGR. Ultrasound Doppler check the blood flow to the placenta and through the umbilical cord to the baby. Reduced blood flow can mean your baby has FGR. You may have repeated ultrasound exams, Doppler studies and other exams. How does FGR handle it? Management depends on how serious the FGR is. This is based on ultrasound (estimated) fetal weight) and ultrasound Doppler (blood flow to the baby), as well as risk factors and the number of weeks of gestation. Treatment may include: Frequent monitoring. This means that you will have prenatal visits more often, ultrasound and ultrasound Doppler exams. You may have other tests. Tracking fetal movements. Your healthcare provider may also ask you to keep track of fetal movements. If so, He or she will give you instructions. Corticosteroid Medicine Hospital stay Early delivery or emergency caesarean section What are the possible complications of FGR? FGR can cause many serious complications. Your baby may need to be delivered early and stay in the hospital. Your baby may have breathing problems, infections, and others problems. Births and death can occur. As your child grows, he or she will be a higher risk of heart problems and blood vessels. How can FGR be prevented? FGR can occur in any pregnancy. But some factors, such as smoking cigarettes or alcohol or use of medicines, increase the risk of FGR. Regular and early prenatal care Healthy diet and constant weight gain help prevent FGR and other problems. When should I call my healthcare provider? Make sure your healthcare provider knows your health history. If you're counting fetal movements and find that the number has decreased, let your health care provider I know. And if you notice other changes or have concerns about your pregnancy, Call your healthcare provider. Key points on restriction of fetalFGR growth is a condition in which the baby is less than expected for gestational age. Many factors increase the risk of FGR. They may be related to the placenta, mother, or baby. Estimating fetal weight with ultrasound is the best way to identify FGR. If the FGR is diagnosed, it should be monitored closely. Next steps Tips to help you get the most out of a visit to your healthcare provider: Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen. Before your visit, write questions you want to answer. Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider says You. On the visit, type the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medication, treatment, or evidence. Also write any new instruction your provider gives you. Know why a new medication or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are. Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways. Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results can mean. Know what to expect if you do not take the medication or have the test or procedure. If you have a follow-up appointment, type the date, time and purpose for that visit. You know how you can contact your provider if you have questions. Medical journals: Doctors: Doctors and ServicesDo2021 University of Rochester Rochester Medical Center, NYSee: K2

Complications of the placenta

Increased blood flow in the basement of the placenta, and a... | Download Scientific Diagram

Placental Insufficiency, Medical Malpractice, and Birth Injury

Placental transfusion through cord milking with an intact cord (I-UCM)... | Download Scientific Diagram
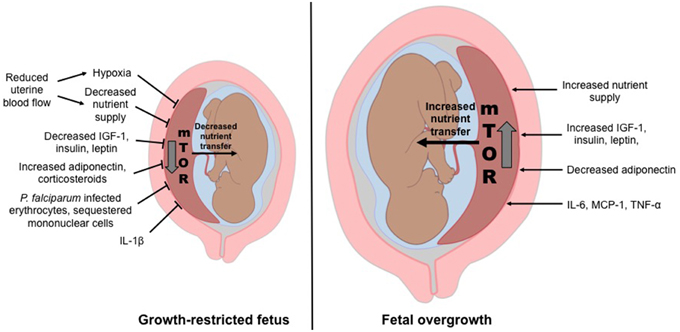
Frontiers | Placental Responses to Changes in the Maternal Environment Determine Fetal Growth | Physiology

What to eat for a healthy placenta | Cells4Life

Placental circulation

How Can I Increase Blood Flow to Baby? - New Beginnings Doula Training

Placental Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis

The Prescient Placenta | The Scientist Magazine®

Schematic representation of blood flow through the placenta and... | Download Scientific Diagram

Fetal circulation - Wikipedia
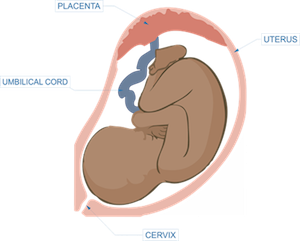
Placental Insufficiency
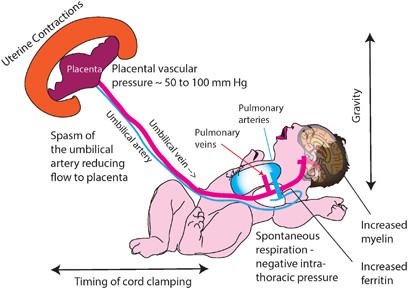
Placental transfusion: a review | Journal of Perinatology
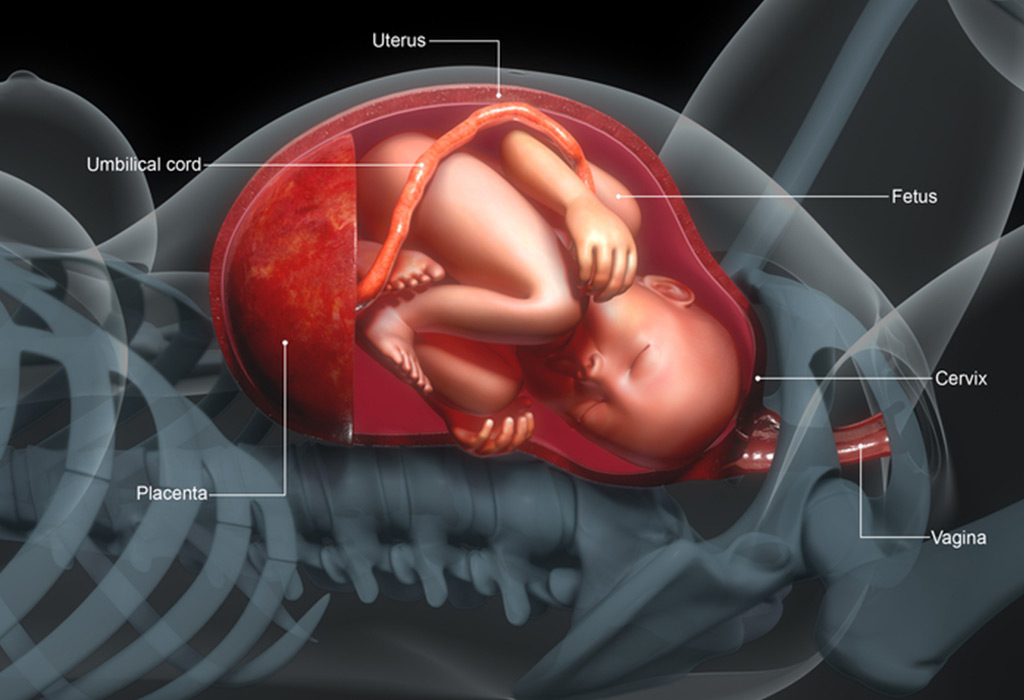
Placental Insufficiency - Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
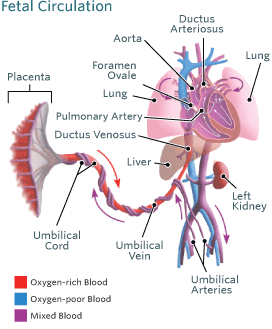
Blood Circulation in the Fetus and Newborn | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia

Establishment of maternal blood supply to the placenta: insights into plugging, unplugging and trophoblast behaviour from an agent-based model | Interface Focus

Uterus Blood Flow - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Oxidative stress throughout human pregnancy and its relation to... | Download Scientific Diagram

Spiral Arteries by The Placenta Lab - issuu

Fetal circulation. The placenta serves as a major buffer in reducing... | Download Scientific Diagram

The placenta: What it is and how it works | BabyCenter
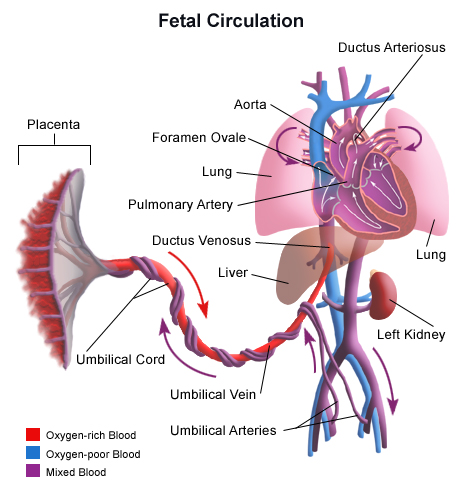
Blood Circulation in the Fetus and Newborn - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center

How To Naturally Improve Circulation During Pregnancy | Walnut Hill OBGYN

Placental Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis

The haemodynamics of the human placenta in utero | bioRxiv

Placental Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Placental blood circulation

The physiology of intrapartum fetal compromise at term - American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology
What disorders can affect the placenta during pregnancy?

The Basics: for the Non-Obstetrician (Section 2) - Respiratory Disease in Pregnancy

Placental Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis

3 Easy Ways to Increase Circulation to Your Uterus - Natural Fertility Info.com Natural Fertility Info.com

Placenta - Wikipedia
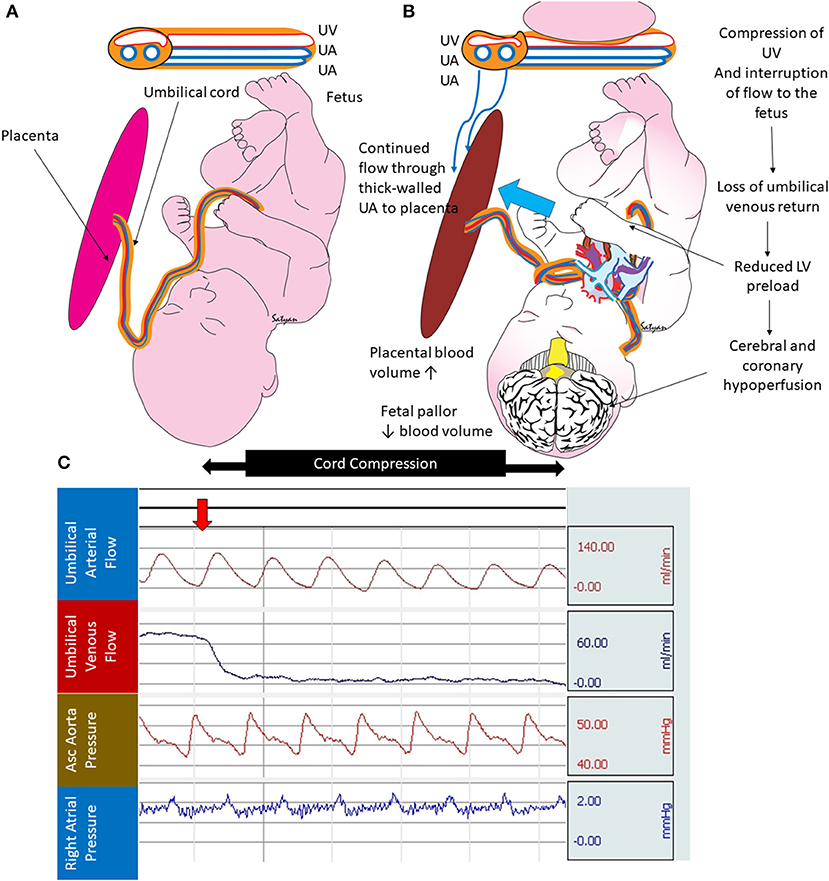
Frontiers | Placental Transfusion for Asphyxiated Infants | Pediatrics

Six key pregnancy hormones and their roles – Compound Interest
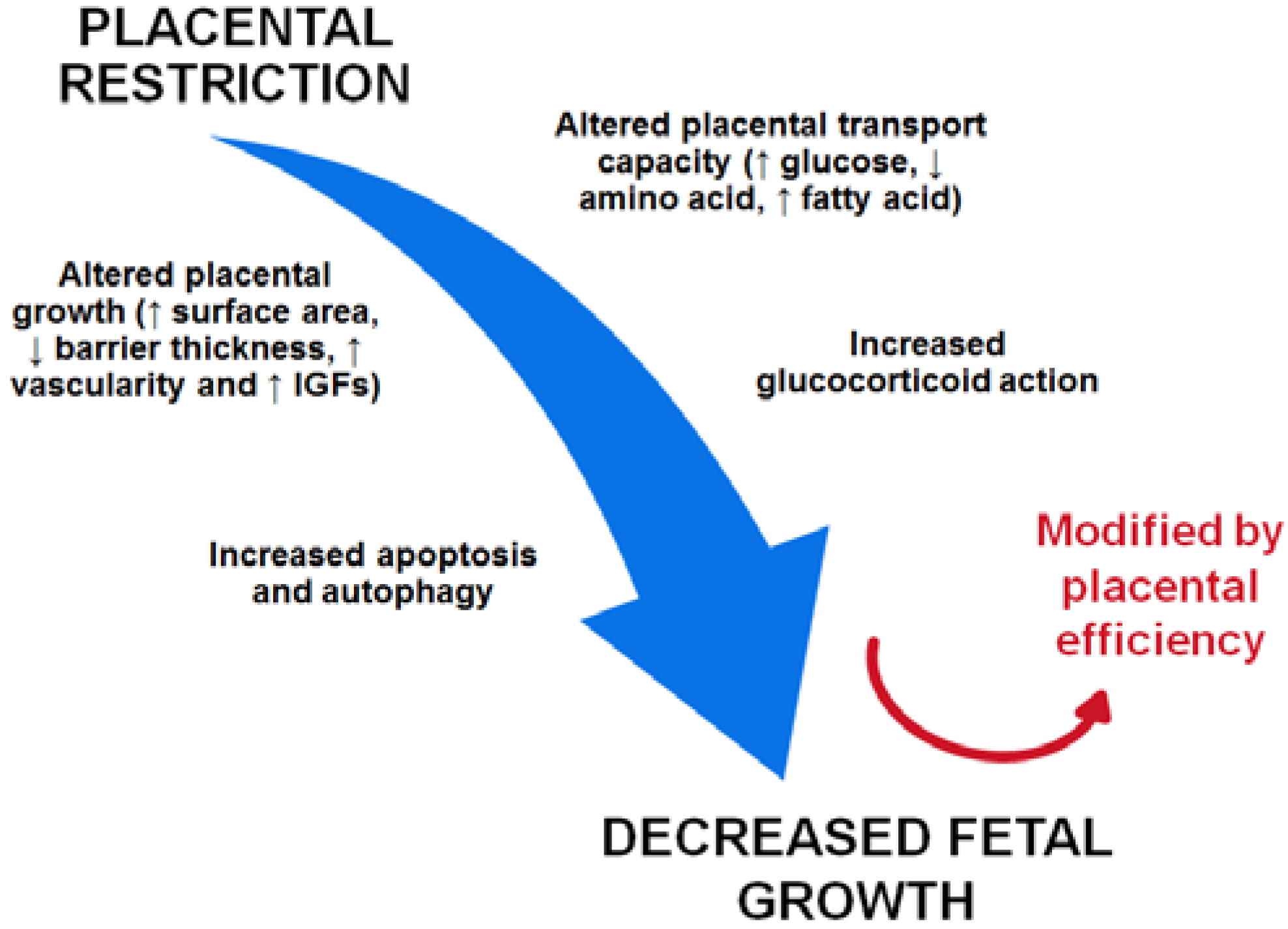
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Placental Adaptations in Growth Restriction | HTML

Human placental mesenchymal stem cells improve stroke outcomes via extracellular vesicles-mediated preservation of cerebral blood flow - EBioMedicine
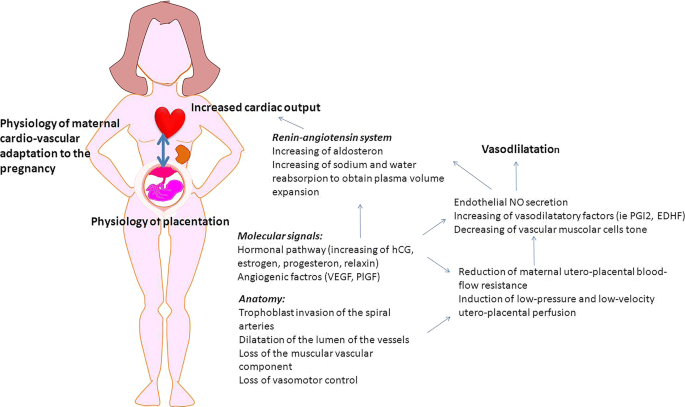
Fetal Growth Restriction: Does an Integrated Maternal Hemodynamic-Placental Model Fit Better? | SpringerLink

Uterine and Placental Blood Flow | GLOWM
Posting Komentar untuk "how to increase blood flow to placenta"